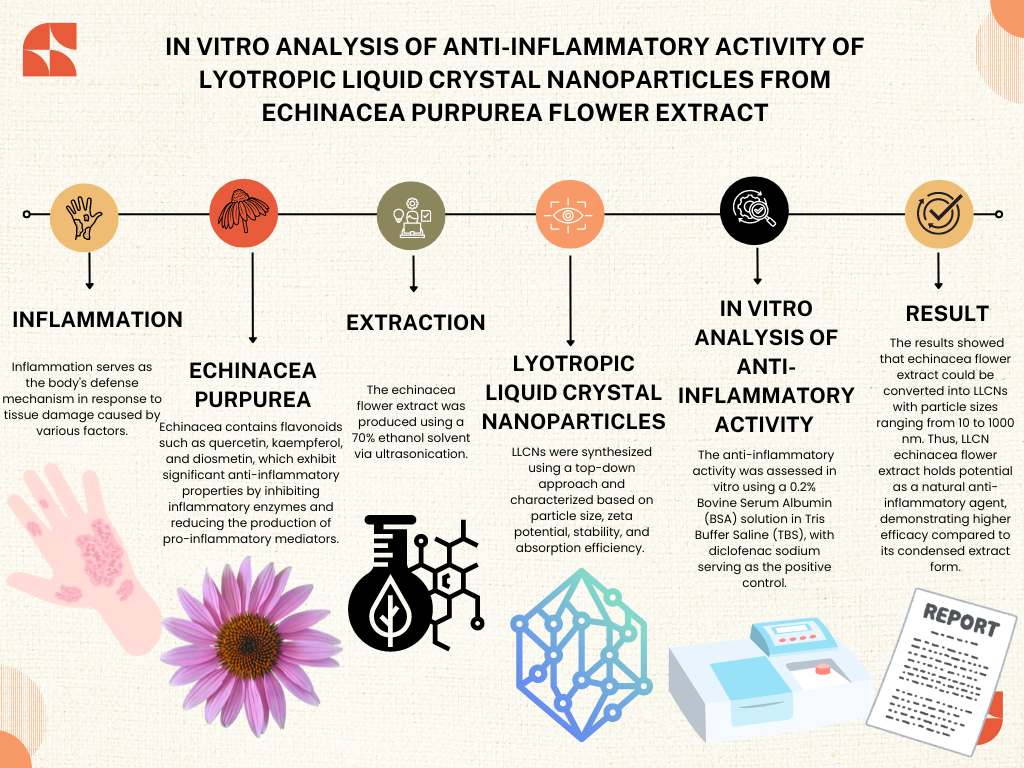
In Vitro Analysis of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Nanoparticles from Echinacea purpurea Flower Extract
Downloads
Inflammation serves as the body's defense mechanism in response to tissue damage caused by various factors. Echinacea contains flavonoids such as quercetin, kaempferol, and diosmetin, which exhibit significant anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting inflammatory enzymes and reducing the production of proinflammatory mediators. This study aims to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effects of echinacea flower extract formulated as Lyotropic Liquid Crystal Nanoparticles (LLCN) and compare its efficacy with viscous echinacea flower extract and diclofenac sodium. Echinacea flower extract was produced using 70% ethanol solvent via ultrasonication. LLCNs were synthesized using a top-down approach and characterized based on particle size, zeta potential, stability, and absorption efficiency. Anti-inflammatory activity was assessed in vitro using 0.2% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) solution in Tris Buffer Saline (TBS), with diclofenac sodium as a positive control. The results showed that echinacea flower extract can be converted into LLCN with particle sizes ranging from 10 to 1000 nm. The LLCN formulation of echinacea flower extract showed stronger anti-inflammatory activity compared to the condensed extract, with activity recorded at 54,660 ppm, IC50 for LLCN at 21,823 ppm, and IC50 for diclofenac sodium at 19,984 ppm. Thus, echinacea flower extract LLCN has potential as a natural anti inflammatory agent, which shows higher efficacy compared to its condensed extract form. This indicates that LLCN technology not only improves the bioavailability, but also the effectiveness of the extract in inhibiting inflammation, thus LLCN has the potential to be applied more widely in the development of natural drugs for anti inflammatory therapy.
Downloads
Copyright (c) 2024 Jurnal Mandala Pharmacon Indonesia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.